Advance tax may seem tricky, but knowing the basics can help you manage your money. This knowledge can also prevent surprises at the end of the financial year. In this blog, we’ll cover advance tax. We’ll explain who must pay it, key deadlines, and the online payment process. We’ll also show you how to calculate your tax liability with a practical example.
What Is Advance Tax?
Advance tax is the income tax you pay in parts throughout the year. This way, you avoid a large payment all at once at the end. It’s a way of paying tax on your income as you earn it, ensuring that your tax liability is spread evenly throughout the year. This method works for different income sources, not just your salary. It includes rental income, capital gains, interest from fixed deposits, lottery winnings, and earnings from freelance or business work.
Who Needs to Pay Advance Tax?
The requirement to pay advance tax applies to a wide range of taxpayers:
- Individuals, Freelancers, and Businesses: If your estimated tax liability (after adjusting for tax deducted at source) exceeds Rs 10,000 in a financial year, you are required to pay advance tax.
- Presumptive Taxpayers: Professionals and businesses using the presumptive taxation schemes under sections 44AD or 44ADA must make their entire advance tax payment in one installment, typically by March 15 (with an option to extend to March 31).
- Senior Citizens: Generally, individuals aged 60 years or more who do not have income from business or profession are exempt from paying advance tax. However, if they are engaged in business activities, the requirement applies.
Key Payment Deadlines
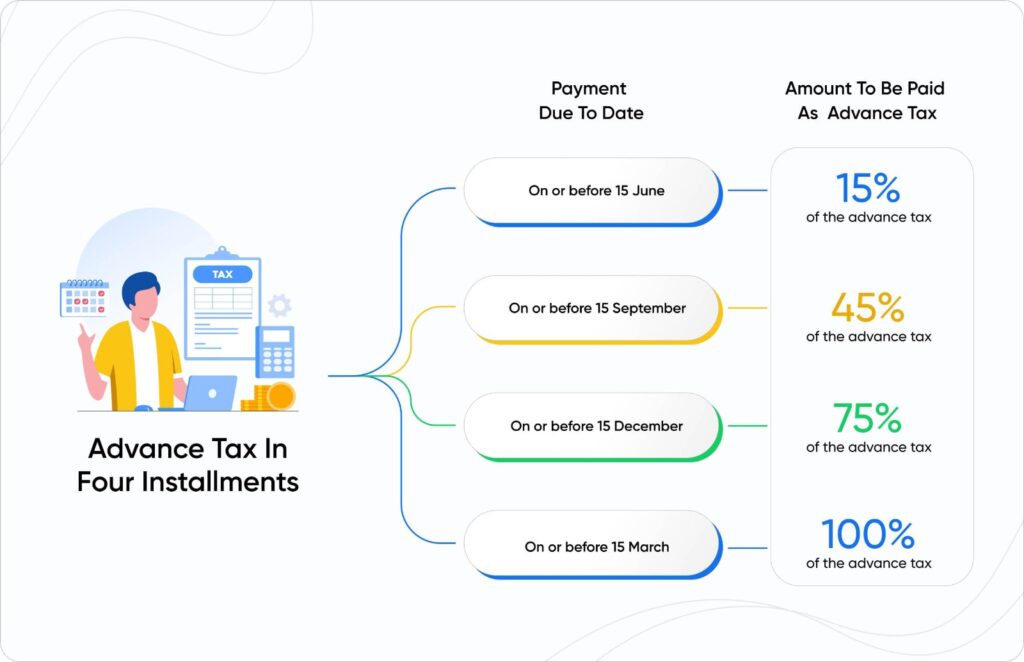
Calculating Your Advance Tax Liability
Calculating your advance tax liability involves several steps:
- Estimate Your Total Income: Sum up all income sources—salary, business or professional income, rental income, capital gains, interest, etc.
- Subtract Eligible Deductions: Deduct amounts available under sections such as 80C, 80D, and other applicable deductions.
- Compute the Taxable Income: Apply the relevant income tax slab rates to your net income.
- Adjust for TDS: Subtract any tax already deducted at source.
- Determine the Liability: If your net tax liability exceeds Rs 10,000. Then you must pay the advance tax in the prescribed installments.
Example: How Advance Tax is Calculated
Let’s illustrate the process with a practical example:
Meet Ajay – A Freelancer
| INCOME ESTIMATION FOR ADVANCE TAX | AMOUNT (Rs) | AMOUNT (Rs) |
| Income from profession: | ||
| Gross receipts | 20,00,000 | |
| Less: Expenses | 12,00,000 | 8,00,000 |
| Income from other sources: | ||
| Interest from fixed deposit | 10,000 | |
| GROSS TOTAL INCOME | 8,10,000 | |
| Less: Deduction under section 80C | ||
| Contribution to PPF | 40,000 | |
| LIC premium | 25,000 | |
| 65,000 | ||
| Deduction under section 80D | 12,000 | |
| TOTAL INCOME | 7,33,000 | |
| TAX PAYABLE | 59,100 | |
| Add: Education cess @ 4% | 2,364 | |
| 61,464 | ||
| Less: TDS | 30,000 | |
| TAX PAYABLE IN ADVANCE (as it exceeds Rs.10,000) | 31,464 |
| ADVANCE TAX PAYMENTS | ||
| Due date | Advance tax payable | Amount (Rs) |
| 15th June | 15% of Advance tax | 4,700 |
| 15th September | 45% of Advance tax | 9,400 (14,100-4700) |
| 15th December | 75% of Advance tax | 9,400 (23500-14100) |
| 15th March | 100% of Advance tax | 7900 (31,400-23500) |
How to Pay Advance Tax Online
The digital era has simplified the process of paying advance tax. Here’s a step-by-step guide to paying your advance tax online:
- Visit the e-Filing Portal: Navigate to the Income Tax Department’s e-filing website and click on the “e-Pay Tax” option.
- Enter Your Details: Provide your PAN and mobile number. Verify your mobile number by entering the OTP you receive.
- Select the Payment Type: Choose “Income Tax” and select the relevant Assessment Year (e.g., 2025-26). Then, opt for “Advance Tax (100)” as your payment type.
- Input Your Tax Details: Fill in your estimated tax details accurately.
- Choose Your Payment Method: Select your preferred payment method and bank.
- Review and Confirm: Verify all the details on your challan, then click “Pay Now.”
- Save Your Receipt: After payment, download and save your tax receipt. This receipt will include your BSR code and challan serial number—details you’ll need when filing your return.
Consequences of Missing Payment Deadlines
Timely payment of advance tax is crucial. Failing to adhere to the deadlines can result in interest penalties:
- Section 234B: If you haven’t paid at least 90% of your tax liability by March 31, you will incur interest on the unpaid amount.
- Section 234C: Delays in meeting the installment deadlines attract a monthly interest charge of 1% on the shortfall.
These penalties are designed to encourage taxpayers to make regular payments throughout the year.
Advance tax is more than just a statutory requirement. It’s a strategic financial tool that helps distribute your tax liability over the year. It will ease the burden of a year-end tax payment. Whether you’re a salaried employee, freelancer, or business owner, understanding and managing your advance tax payments can streamline your tax planning and help avoid unnecessary penalties.
Start early, plan ahead, and leverage online tools and calculators to ensure that your tax payments are accurate and timely. By staying proactive about your tax obligations, you’ll be better positioned to manage your finances throughout the year.